Chemotherapeutic drugs that are frequently used to treat colorectal cancers include:
- 5-Fluorouracil (5-FU) – with or without leucovorin
- Capecitabine (Xeloda®) – an oral prodrug that is converted to 5-FU in the body
- Irinotecan (Camptosar®)
- Oxaliplatin (Eloxatin®)
- Trifluridine and tipiracil (Lonsurf®) – an oral combination product
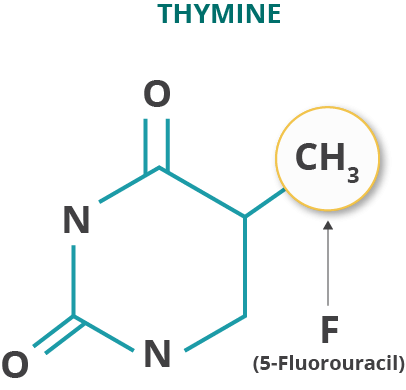
5-FU is a compound that incorporates a fluorine atom into thymine, which is one of the basic building blocks of DNA. It interferes with the synthesis of DNA and, to a lesser extent, inhibits the formation of RNA. This affects rapidly growing cells and may lead to cell death. 5-FU is used in the treatment of patients with adenocarcinomas of the colon and rectum, breast, stomach, and pancreas. It is administered intravenously. In CRC, it is used in combination with other chemotherapeutic agents as a neoadjuvant and adjuvant treatment, and for the treatment of metastatic disease. It is typically given via bolus injection day 1 followed by continuous infusion over 2 days in mCRC combination regimes (eg, FOLFOX, FOLFIRI).
Adverse effects associated with the use of 5-FU include anorexia, nausea, stomatitis, diarrhea, and myelosuppressive effects that result in leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, and anemia. It also may cause hair loss, skin reactions, and hand-foot syndrome.