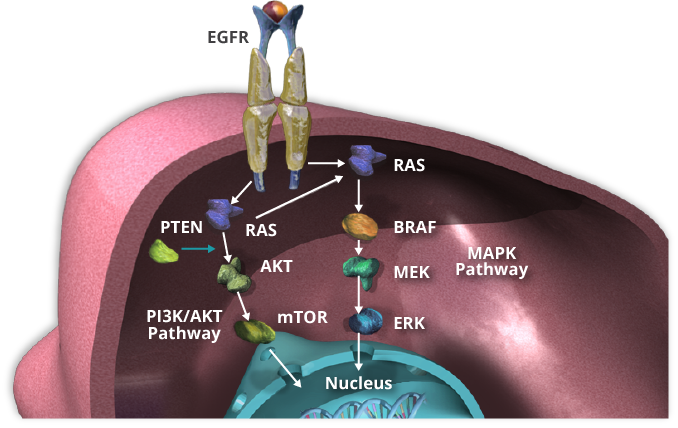
Aberrant activation of proteins within the EGFR, MAPK, and PI3K signaling pathways promote cellular proliferation, differentiation, and survival. This abnormal protein activation, caused by gene mutations to RAS, BRAF, PIK3CA, and PTEN, play a role in affecting the response of CRC to therapy. Thus, molecular testing to identify these mutations is becoming a standard practice for the management of patients with CRC.
Earlier testing approaches focused on one or a few of these gene mutations. However, the current need for information on multiple molecular markers is leading to a greater use of targeted next-generation sequencing (NGS) cancer gene panels. These panels can assay from a few to hundreds of genes that are known to play a role in the development of cancer. Tap the arrow to learn more about specific genetic mutations.