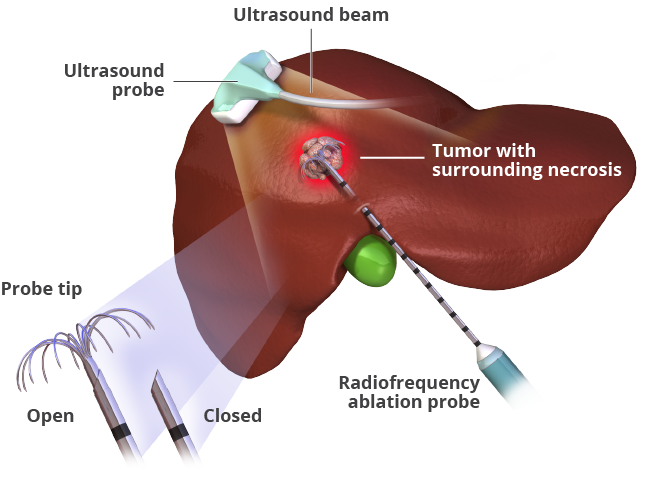
Ablation is a treatment that destroys small tumors (<4 cm across), while embolization is a technique that blocks or reduces blood flow to a tumor. These techniques may be used to treat small metastatic liver tumors after the primary tumor has been removed, and in patients who are not candidates for surgery. A number of different types of ablation therapy have been used including:
- Radiofrequency ablation – the use of high-energy radio waves to kill cancer cells
- Microwave ablation – microwaves are applied to tumor cells to destroy them with high temperatures
- Ethanol (alcohol) ablation – concentrated alcohol is injected into tumor cells to kill them
- Cryosurgery (or cryoablation) – a probe is used to freeze and kill cancer cells
Radiofrequency Ablation
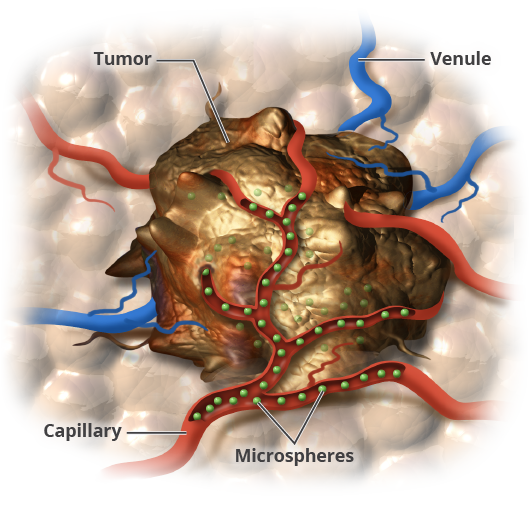
Embolization techniques may be used when liver tumors are too large to be treated with ablation. With arterial embolization, a catheter is threaded into the hepatic artery and manipulated into a position close to the tumor. Tiny particles are then injected into the blood vessel to plug it up and reduce the blood supply to the tumor. In a variation of this technique known as chemoembolization, the particles injected contain chemotherapeutic drugs, which are slowly released into the tumor. Another variation known as radioembolization incorporates radioactive yttrium-90 into the particles. Once injected, the particles emit radiation close to the tumor for several days, killing the cancer cells.
Radioembolization Therapy