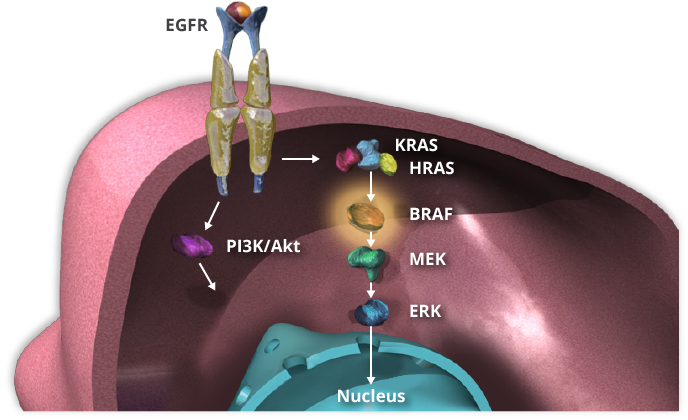
Up to 10% of colorectal cancers have a BRAF V600E mutation. These mutations are generally limited to tumors that do not have RAS mutations. The protein product of the mutated BRAF gene is constitutively active, causing continuous activation of the MAPK signaling pathway. It is downstream of both EGFR and RAS signaling proteins.
BRAF V600E mutations are more common in women, in older patients, and in those whose tumors are on the right side of the colon (see previous discussion). They often have high-grade histology and microsatellite instability, and frequently spread to the peritoneum. Patients with these mutations have a poor prognosis. However, not all BRAF mutations have the same clinical characteristics. Tumors with non-V600 BRAF mutations are often associated with a favorable prognosis. Tap the arrow to learn more about specific genetic mutations.